If companies are searching for smarter ways to avoid costly disruptions, the benefits of predictive maintenance are difficult to ignore. New research from IDS-INDATA highlights the scale of this problem, claiming that manufacturers across the UK and EU are predicted to lose over £80 billion due to unplanned downtime. In this article, we explore the key predictive maintenance advantages and disadvantages, its use cases, and best practices.
We live in a time when technology can solve more business issues than ever before. The latest advancements can offer companies a competitive edge and significant improvement to their processes. Today we will cover the predictive maintenance advantages and disadvantages for organizations and the ways to protect valuable assets and save on resources with the help of modern approaches like preventive and predictive maintenance, as well as powerful machine learning technology.
What is predictive maintenance, and what is its role?
On August 8, 2016, Delta Air Lines lost power at its operations center in Atlanta due to an electrical equipment failure. Computers used for booking passengers were down for nearly five hours. The result? Nearly 1,000 flights were canceled on the outage day and another 1,000 over the next two days. The financial damage reached close to $150 million, plus additional money on refunds and offering vouchers to clients for future travel.
This example illustrates the massive downtime costs for organizations. The haul in production can be a massive factor that reduces productivity or stops the manufacturing processes entirely. Plus, add here the adverse effect for reputation.
Predictive maintenance (PdM) offers a much smarter approach. Its goal is to continuously monitor equipment state in order to predict anomaly behaviors that may lead to costly failures and take actions to prevent those failures ahead of time.
In order to do that, the system is constantly monitored, and analysis is being made based on data collected from various IoT sensors. As a result, the functioning of your equipment will be optimized, and the repair costs will be reduced. While it does not entirely replace traditional maintenance approaches, it is an excellent addition to the overall maintenance process.
Benefits of predictive maintenance
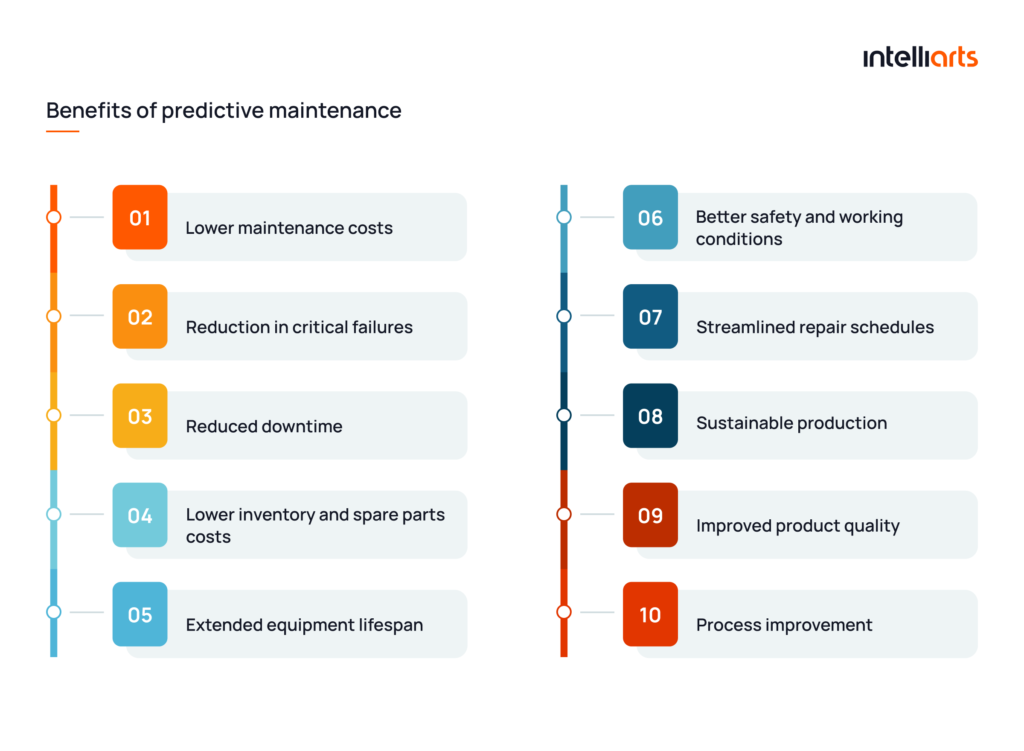
By its definition, predictive maintenance is an approach to equipment management that brings advantages across costs, safety, and operational efficiency. Let’s consider the benefits of predictive maintenance in manufacturing in detail:
Lower maintenance costs
Predictive maintenance can reduce maintenance costs by up to 50%. With PdM, businesses don’t waste costs on regular maintenance activities, as these are performed only when truly needed. This targeted approach leads to substantial predictive maintenance savings by minimizing labor, materials, and time spent on redundant tasks.
Besides, companies save on diagnostics since PdM systems warn about potential equipment health issues in advance. These efficiencies contribute to a higher predictive maintenance ROI, as businesses reduce operational expenses while maintaining or even improving asset performance.
Reduction in critical failures
Among other benefits of predictive maintenance, businesses can also reduce the number of critical equipment failures by up to 90%. The system continuously tracks performance indicators, and companies get informed about asset degradation and can interfere long before the actual failure occurs.
Reduced downtime
Downtime related to the actual repair process will also be lower because you could identify the components that might break down in the first place. The complexity and cost of maintenance decrease as you only replace parts that are causing the failure and not all the parts that might have been broken during the failure.
Lower inventory and spare parts costs
Compared to preventive maintenance, PdM minimizes the need to stockpile spare parts. A manufacturer performs maintenance activities only when they’re actually needed, and theoretically, you should buy the new parts more rarely.
Streamlined repair schedules
Knowing the actual health status of equipment is another thing to consider among the benefits of predictive maintenance. This helps manufacturers plan repair shutdowns. PdM transforms emergency fixes into scheduled events, allowing teams to align maintenance activities with production goals and minimize operational disruption.
Extended equipment lifespan
For expensive machinery, predictive maintenance services can save you money on extending the life of particular parts. PdM grants you fewer machine breakdowns and timely help, so the equipment works longer and becomes more resilient.
More sustainable production
By reducing unnecessary part replacements and minimizing waste, PdM supports sustainability. As companies extend equipment lifespan and optimize maintenance schedules, they lower their environmental footprint and make more efficient use of resources.
Better safety and working conditions
Potentially saving employees’ lives caused by destructive failures is also among the advantages of predictive maintenance. If you know about potential breakdowns and react to them quickly, you could also warn the operators and improve the working conditions.
Improved product quality
Consistent equipment performance directly influences product quality. Predictive maintenance helps avoid sudden breakdowns or gradual wear that could affect production standards, resulting in fewer defects and more uniform output.
Process improvement
PdM systems often collect and analyze performance data, helping identify unusual patterns or deviations in the production process. These insights can highlight emerging issues early or point to areas where process optimization is needed.

Predictive maintenance disadvantages
While PdM brings long-term benefits, it also comes with certain challenges, especially in the early stages of implementation. Understanding the disadvantages of predictive maintenance can help make informed decisions and plan PdM strategies more effectively.
High initial costs
One of the primary barriers to adopting PdM is the upfront investment. Here we can mention expenses on IoT, data collection, storage, and other related infrastructure, which can be especially costly for small and medium-sized manufacturers.
Complexity
PdM requires a complex system setup with a high level of IT expertise. Businesses spend much time and resources hiring and retaining a qualified workforce. That said, this complexity can work to your advantage when partnering with an experienced technology provider. Our team at Intelliarts specializes in software development for manufacturing — we can help you build or scale your predictive maintenance solutions from the ground up.
Data accuracy
The effectiveness of any PdM solution depends heavily on the quality and accuracy of the collected data. Incomplete, noisy, or poorly labeled data can lead to false alarms or missed failures. The workable solution here is to pay attention to robust data collection and continuous model improvement.
Employee training
To some extent, turning monitoring into predicting requires a cultural shift. Maintenance teams used to traditional methods may feel reluctant to trust machine-generated insights. Proper training and internal communication are key to solving this problem.
Predictive maintenance use cases in different industries
To understand the benefits of predictive maintenance better, let’s also review specific examples of how PdM helps minimize downtime and optimize asset performance across various sectors:
Oil and gas
In this industry, PdM is crucial for preventing equipment failures, which are costly and can lead to severe environmental consequences. The 2025 study describes the use of an ensemble learning model that assesses the health status of oil and gas equipment and predicts its remaining useful life. In the long run, the model can help optimize maintenance schedules and reduce unnecessary costs.
Manufacturing
Manufacturers are leveraging PdM to enhance operational efficiency and reduce industrial downtime. One of the most illustrative examples is predictive maintenance of hydraulic systems. As part of this solution, the Intelliarts team built four machine learning models to predict the degradation level of the hydraulic components: cooler, valve, pump, and hydraulic accumulator.
Another example is the deployment of predictive maintenance by Alcoa, the aluminum smelter in Iceland. The implementation of PdM reduced unplanned downtime by up to 20% and helped achieve full ROI in 4-6 months. Now the manufacturer is planning to scale its effort to 1000 more assets as well as to other sectors in their business.
Looking for more interesting examples? Check this guide on predictive maintenance in manufacturing.
Energy
Reliability of infrastructure is truly important in the energy sector, and this is what predictive maintenance can provide to energy businesses. A prolific example is when NextEra Energy implemented advanced analytics for gas turbine maintenance, which resulted in improved performance and reduced unplanned outages. The company achieved impressive results with a 23% reduction in downtime and $25 million in annual maintenance cost savings.
Healthcare
In healthcare, predictive maintenance increases the availability and reliability of medical equipment. The survey of predictive maintenance in healthcare systems highlighted how important data-driven strategies are to predict equipment failures in order to improve patient safety and reduce maintenance costs.
Transportation
The transportation industry uses PdM to maintain vehicle fleets and infrastructure. For instance, PdM can help monitor the health of transportation systems by analyzing data from vehicle sensors. Fleet operators that rely on PdM systems report a 30–50% reduction in unexpected breakdowns, saving costs and improving vehicle uptime. A great example is the use of PdM in bus fleets, where real-time monitoring systems can detect anomalies such as unauthorized tire changes and increase passenger safety.
Automotive
As for the automotive industry, it applies PdM to monitor vehicle components and predict failures. In one case study, a major car manufacturer avoided $0.5 million in unplanned downtime thanks to a predictive maintenance solution. The latter allowed for data-driven operational decisions and maximized equipment lifespan and reliability.
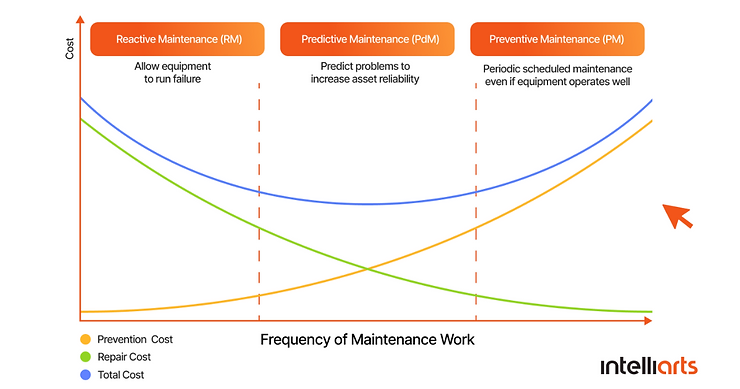
Difference between reactive vs. preventive vs. predictive maintenance
Depending on the extent of a system failure, there are multiple ways to solve the situation. Let’s take a closer look at the different types of system maintenance.

Reactive maintenance
This type of maintenance happens after the system or equipment breaks down. All the focus goes to restoring everything as close to “normal” condition as possible. Obviously, emergency fixes are far more expensive compared to planned maintenance. Another reason for the high cost of reactive maintenance is the fact that critical outages are most likely to happen during peak hours, disrupting processes when they matter the most. The necessity to fix everything as fast as possible may lead to additional expenses on hiring additional services and buying unplanned equipment.
In comparison of reactive maintenance vs. preventive maintenance, reactive is a more short-term approach with unpredictable costs and frequent operational disruptions.
Best fit for:
- Non-crucial equipment
- Equipment with low repair costs
- Easily fixed equipment
Not suitable for situations:
- When equipment failure may lead to safety or security issues
- When the repairment process is time-consuming
- When equipment must be available 24/7
- When equipment is very expensive
Preventive maintenance
This is a popular approach when companies plan regular maintenance tasks to keep equipment in working condition. The key difference from reactive maintenance is the fact that you have scheduled repairments. The interval of the checkups may vary dramatically, from once in a few days to annual tune-ups.
Talking about the difference between preventive and predictive maintenance, it relates to how maintenance is scheduled: based on time or usage intervals in preventive maintenance or real-time data in predictive maintenance. Therefore, preventive maintenance risks performing unnecessary maintenance or failing to catch unforeseen breakdowns.
Best fit for:
- Equipment prone to wear and tear over time
- Systems with predictable failure patterns
- Situations where failure modes can be prevented (and not increased) with regular maintenance
Not suitable for situations:
- When equipment may have random failures that are unrelated to maintenance or maintenance frequency
- When over-maintenance leads to unnecessary costs
Predictive maintenance
Predictive maintenance uses real-time data from sensors to assess equipment health and predict failures before they occur. Since it relies on data-driven insights, PdM is more precise and cost-efficient than other types of maintenance. When comparing preventive vs. predictive maintenance, predictive offers a smarter, more efficient way to manage assets.
Best fit for:
- Companies with IoT-equipped machinery that allows data collection
- Businesses seeking to reduce downtime and maintenance costs through prediction
- Environments where failure prevention is critical to operations
Not suitable for situations:
- When you don’t have any IoT sensors that provide diagnostic information about your equipment – in that case it’s better to start with an equipment upgrade
In terms of frequency of maintenance, the three methods could be compared as:
Here is a visual representation of what happens in these three methods when the maintenance is being done:
While requiring more IT expertise and some additional expenses, predictive maintenance is the most effective method for machine learning failure prediction and saving lots of money.
Best practices for implementing predictive maintenance solutions
1. Start with proper data collection
Your predictive maintenance strategy is only as good as the data it’s based on. The first thing you need to do is to set up a proper data collection process, which will allow you to get all the necessary information, including data from equipment and sensors, as well as overall system data over a certain period of time.
2. Choose the right predictive system
Next, you need to build a system that will make conclusions and predictions based on collected data. The number of parameters that are usually being collected will be impossible to process by humans. There are two most popular ways to go with this system, creating a rule-based AI system or using machine learning (ML) models. Both approaches have their own advantages and disadvantages of predictive maintenance.
Rule-based artificial intelligence systems
These systems generate pre-defined outcomes according to rules programmed by human experts. Rule-based systems use “a set of rules” and “a set of facts” to make statements. The best usage of this approach is when you need speedy outputs, have a very high risk of error (however, ML systems can work in those scenarios as well), and don’t plan to implement machine learning in the future.
On the drawback side of rule-based AI systems:
- Are costly and time-consuming in implementation
- Require complete knowledge of the behavior of equipment
- Don’t perform well with previously unknown faults
Machine learning systems
The key difference is that ML-based systems define their own set of rules that are based on data inputs. They could take the correct data and work based on a probabilistic approach. But why is it such a powerful alternative to a rule-based system?
- The advantage of predictive maintenance lies in ML systems’ ability to learn and adapt to new conditions, compared to static rule-based systems with a deterministic approach
- Rule-based systems are limited to certain business logic. When the event occurs outside this business logic, the rule-based system will ignore this event. Machine learning algorithms are always aware of the “normal” state of the system. When something abnormal happens, the ML system will detect it
- Machine learning systems can detect patterns in abnormal behavior, while rule-based systems will look only for previously set scenarios
- Compared to straightforward rule-based systems, ML systems can be used in more complex cases. Additionally, when there is no simple and obvious way to solve a specific challenge, a machine learning system could be the only solution to the problem
- When the situation and the type of data are changing fast, it could be ineffective to constantly rewrite business logic for the rule-based system. The ML approach will be able to keep up with the changes
- There can be possible conflicts between rules when their number grows exponentially. At some point, you may lack the computing power to control all possible combinations of rules in your system or have the challenge of managing all the rules properly
Read also: Predictive Maintenance Using Machine Learning and Predictive Maintenance Using Deep Learning
3. Start with a pilot project
Predictive maintenance and ML can feel overwhelming at first. Instead of trying to overhaul your entire operation, launch a small-scale pilot project with one or two critical assets. This will let your team build confidence, fine-tune the process, and identify early challenges without major risk.
4. Scale up when ready
Once the pilot is successful, don’t wait too long to scale. PdM systems are scalable by nature — and businesses can go from a few connected machines to a fully operational smart factory in just 6 to 12 months. The longer you wait, the more likely operational gaps (such as missing documentation or poor staff training) will slow down broader implementation.
5. Get expert support
Successful implementation often requires technical expertise that goes beyond your in-house capabilities. Partnering with a skilled ML team ensures you avoid missteps and get the most out of your predictive maintenance investment. A qualified team can help with model development, infrastructure setup, and long-term optimization.
Conclusion
The maintenance of assets is a major challenge for organizations across the world. The right choice of maintenance strategy can save an enormous amount of money that could be spent on the future growth of an organization.
Each mentioned approach can be used in a certain scenario, however, predictive maintenance with the power of machine learning technology is probably the most efficient way to deal with this challenge. For sure, you can’t completely eliminate reactive and preventive maintenance from your processes because some incidents will still happen, and your equipment requires regular maintenance and check-ups. However, investing your time and resources into predictive maintenance will help to reduce the number of unfortunate incidents and maintain the equipment in top condition and with lower costs.
Looking ahead, innovations in IoT sensors, real-time data analytics, and the integration of digital twins are further transforming how predictive maintenance is implemented. And this should also be listed among predictive maintenance benefits. AI models are becoming more accurate and scalable, making it easier to move toward fully autonomous maintenance systems.
We at Intelliarts love to help companies solve the challenges with data strategy design and implementation, so if you have any questions related to ML pipelines in particular or other areas of data science consulting services — feel free to reach out.
FAQ
What is the primary goal of predictive maintenance?
The main goal of predictive maintenance is to predict equipment failures before they occur. As a result, a business can perform maintenance at the right moment — neither too early nor too late.
Speaking about the benefits of predictive maintenance, how does predictive maintenance save money?
Predictive maintenance saves money by helping businesses avoid expensive emergency repairs, unnecessary routine checkups, and extended production downtimes. Instead of replacing parts too early or reacting to complete failures, maintenance happens only when needed.
What technologies are involved in predictive maintenance?
Predictive maintenance includes but is not limited to oil analysis, thermography checks, vibration analysis, and acoustic monitoring. Besides, you can build a rule-based or machine-learning-powered predictive maintenance system.