The global smart grid market is forecasted to surpass $130 billion by 2028. It’s no wonder considering that the related but more established renewable energy market is worth nearly $1.1 trillion as of 2023 and is predicted to grow twofold over the next 7 years. It all boils down to the fact that smart usage of electricity in the form of IoT smart grid is a rising trend that can be exploited by various technology, energy, utility, and IoT companies.
Read also: AI in the renewable energy market
In this article, you’ll discover how smart grid works, why it’s better than traditional grids, and where is the connection between IoT and smart grid technology. On top of that, you’ll find IoT based smart grid systems and IoT applications in smart grid. Finally, you’ll learn about the potential future of smart grid technology in IoT and the step-by-step flow for building IoT-enabled smart grid solutions with Intelliarts.
How does the smart grid work?
For starters, let’s familiarize ourselves with the main concept related to the topic.
A smart grid is an electrical grid that uses digital technology to monitor and manage the transport of electricity from all generation sources to meet the varying electricity demands of end users.
Smart grids are an enhancement over traditional power grids by incorporating a range of technological capabilities, which will be detailed in the below sections.
It’s essential to understand that smart grids are not only about the management of electricity. At the modern-day level, smart grids can provide plenty of data, both technical and business. Among other things, information provided via smart grid can be used for empowering IoT tech.
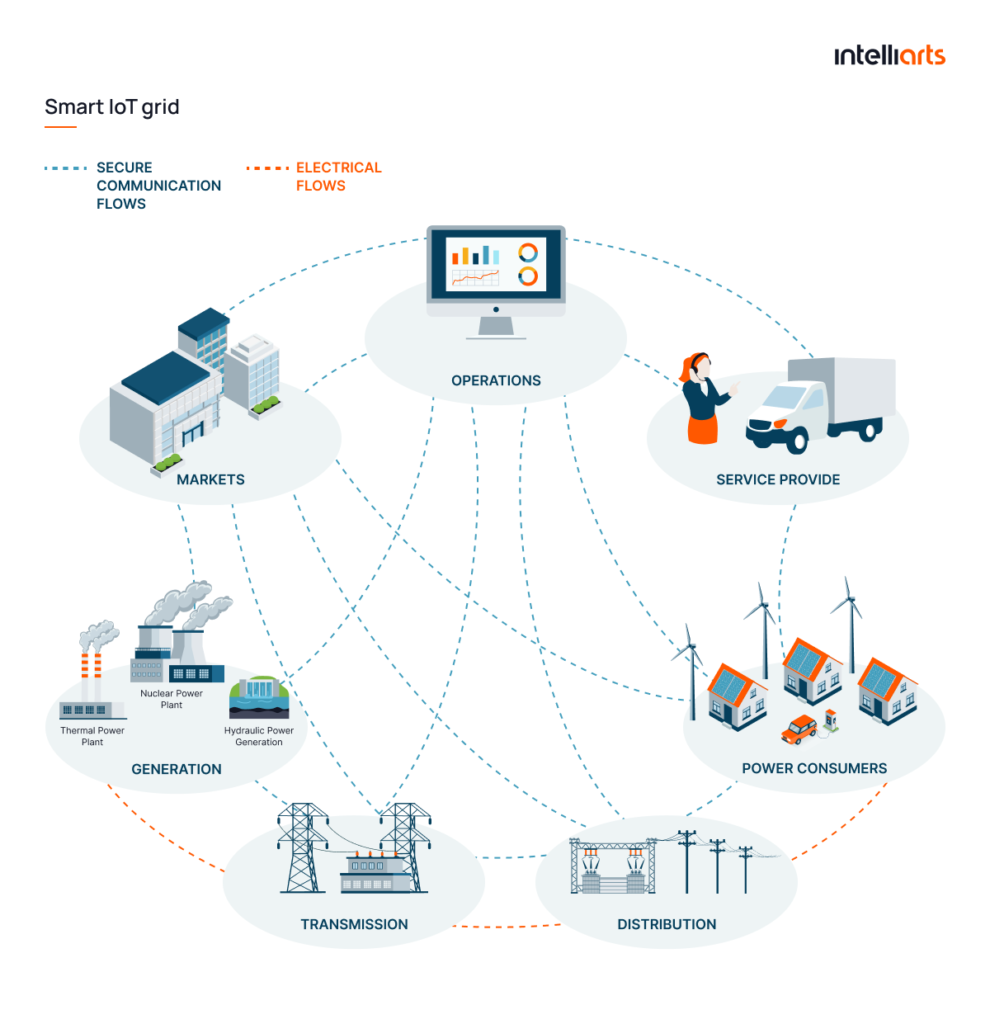
Wrapping everything together, here’s how the smart grid operates across all procedures involved in the regular power cycle intended to manage electrical resources:
- Generate: Smart grids facilitate the integration of diverse generation sources, including renewables, ensuring a flexible and sustainable energy supply.
- Distribute: They employ advanced communication technologies to dynamically manage the distribution of electricity, enhancing the reliability and efficiency of power delivery.
- Use: Smart grids enable real-time monitoring and control of energy consumption, allowing consumers to use electricity more efficiently through smart appliances and meters.
- Control: These grids utilize automated control systems to respond instantly to changes in energy demand and supply, maintaining grid stability.
- Store: Smart grids incorporate energy storage solutions that can store excess energy during low demand and release it during peak times, optimizing energy usage.
Why are smart grids better than traditional grids?
As stated previously, smart grids are the advancement of traditional grids. They incorporate a range of technological capabilities allowing for better electrical resources management. Examples of such tech advancements include:
- Smart meters
- Smart appliances
- Distributed energy resources (DERs)
- Demand response technologies
- Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI)
- Energy storage systems
- Grid automation technologies
- Real-time monitoring and control systems
- Communication networks
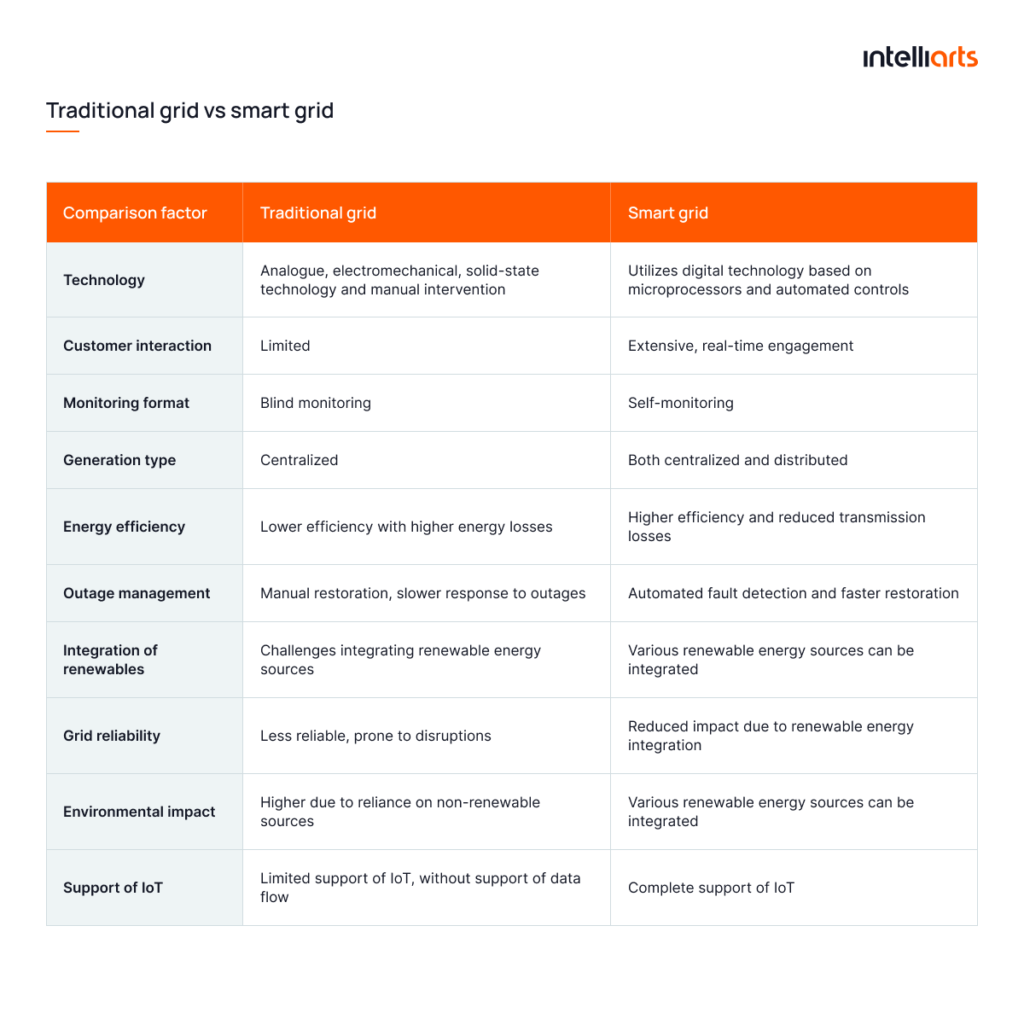
You can discover what such an improvement in the grid technology results into from the comparison table below:
How IoT works in smart grid tech
From a certain perspective, the usage of smart electricity management instruments combined with IoT devices is what makes a traditional grid a smart grid.
Above all, smart grids feature a bi-directional flow of information between consumers and utility companies.
Moreover, the listed above IoT devices, both those operating on energy and those measuring all factors related to management and consumption generate lots of data.
It all boils down to the fact that smart grids give providers a complete overview of the consumption of electricity. It may not sound like smart grids in IIoT provide plenty of useful information, but in reality, the insights derived from such information are vast. Here are some examples of smart grid and IoT:
- Real-time usage
- Time-of-day, seasonality, and other patterns of usage
- Condition data
- Outages and issues
Now it’s time to move to exact use cases of exploiting such data in business.
You may also be interested to discover the usage of IoT in supply chain management in another blog post by Intelliarts.
What are IoT applications in smart grid
So, using the vast data from monitoring sensors in the smart grid, it’s possible to enhance IoT usage and energy management in these ways:
#1 Solar farm monitoring
Solar farm monitoring systems utilize smart grid IoT to continuously track and analyze solar panel performance. This includes monitoring:
- Weather conditions
- Energy output
- Panel efficiency
Data collection helps to optimize energy production and predict maintenance needs, improving overall farm reliability and efficiency. Businesses from manufacturing, energy, and agriculture can benefit from this opportunity the most.
You can discover more about how solar farm monitoring works from the video below:
Read also how implementation of IoT in solar energy systems enhances real-time monitoring and optimization, contributing significantly to grid efficiency.
#2 IoT-based electric vehicle (EV) charging
Such IoT-based systems enable smart management of charging stations. These systems can adjust charging rates based on grid capacity and electricity pricing, provide real-time availability updates, and integrate with user apps for enhanced accessibility, EV energy consumption monitoring and usage tracking.
This IoT in EV application is of the most use for energy, logistics, and transportation companies.
#3 Battery monitoring
Battery monitoring systems use IoT technology to track battery health, charge levels, and performance metrics in real time. This results into:
- Optimal battery usage
- Prolonged lifespan
- Better safety and lower risks of potential failures
This can be used for both stationary and mobile devices operating on energy supplied by an IIoT smart grid. Battery finds vast usage across various business sectors with offline sites, so basically any business utilizing rechargeable batteries can take advantage of battery monitoring.
#4 Smart meters
Smart meters are IoT devices that provide detailed and real-time data on electricity usage directly to consumers and utilities. They support dynamic pricing, enhance energy consumption tracking, and enable more precise billing and energy usage forecasting. Smart meters are of the most usage for energy and IoT companies.
#5 Predictive maintenance
Predictive maintenance in smart grids employs IoT sensors to monitor equipment conditions. This approach detects early signs of wear or malfunction, allowing for timely maintenance that minimizes downtime and extends asset life, thereby reducing operational costs. Predictive maintenance in smart grids can be used by businesses in manufacturing, logistics, transportation, energy, IoT, and other sectors.
To explore how this technology benefits the manufacturing industry, check out our detailed guide on predictive maintenance for manufacturing.
#6 Energy supply smart management
Energy supply smart management leverages IoT to dynamically control and optimize power distribution based on real-time demand and supply data. This helps with the following:
- Improve grid stability
- Reduce energy wastage
- Ensure a consistent, cost-effective energy supply
Smart energy supply management is critical, especially during notable spikes in electricity usage. By incorporating an IoT smart energy grid project, the regulation of power distribution during such events helps maintain grid integrity and prevents complete shutdowns. This application of IoT in the smart grid is particularly valuable to energy, utility, and IoT companies.
Real-life applications of smart energy grid using IoT you should know about
Now, when you understand what’s the use of IoT in smart grids, let’s explore smart grid technology in real life through concrete examples of how companies are applying it:
EV charging solution provider: OpenADR implementation for load management success story by Intelliarts
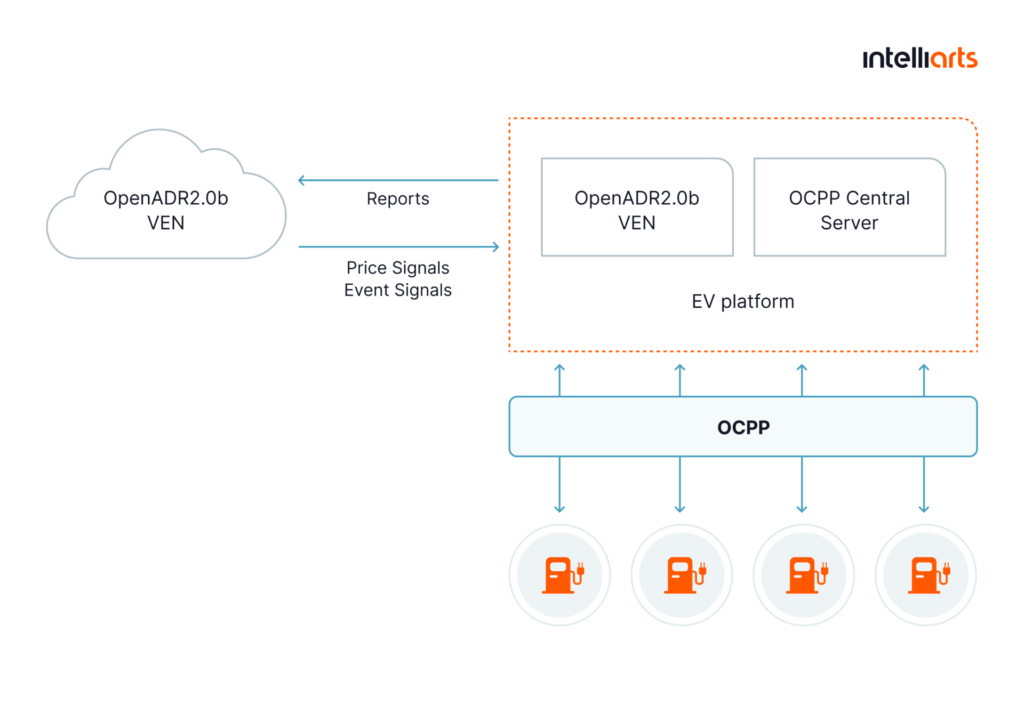
In this case, Intelliarts’ customer, which is the company that sells modern EV charging solutions, needed help with the mitigation of the risk of smart grid overload in their EV charging infrastructure. To enable this, Intelliarts implemented the OpenADR 2.0b specification that allows it to dynamically manage electricity demand in real-time, mitigating spikes in consumption.
The OpenADR protocol implementation was a big step forward. As a result of the project, Intelliarts’ customer achieved increased energy efficiency, better grid reliability, cost-saving, and eco-friendliness of their EV infrastructure.
Lumin: Residential energy management success story by EcoTech innovations
Lumin, a company specializing in energy management solutions for residential properties, sought to enhance homeowners’ ability to manage and reduce their energy consumption efficiently. To address this, EcoTech Innovations developed an integrated smart panel system equipped with IoT technology and data analytics tools.
At the end of the project, EcoTech Innovations delivered a comprehensive solution, known as the Lumin energy platform. The solution enabled Lumin’s customers to achieve significant cost savings, reduce their carbon emissions, and facilitate the easier adoption of green energy solutions. The system also provided capabilities for detailed energy consumption management.
Cisco: Grid modernization success story with BC Hydro by TechGrid Solutions
In this scenario, BC Hydro, a major utility provider, faced challenges in updating its ageing grid infrastructure to improve efficiency and reliability, particularly in incorporating IoT and smart grid technologies. In partnership with TechGrid Solutions, Cisco undertook a project to overhaul BC Hydro’s grid management system. The focus was on implementing advanced smart metering and analytics technologies to enhance the utility’s operational capabilities.
By the project’s end, TechGrid Solutions, leveraging Cisco’s technology, had successfully equipped BC Hydro with a smart grid system. The modernized grid not only improved the reliability and efficiency of electricity supply to consumers but also supported the integration of renewable energy sources, setting a new standard for utility operations in the industry.
The future of smart grids with IoT
In the future, smart grid applications in IoT could enable entirely automated energy systems where homes and buildings adjust their own power consumption in real-time based on usage patterns, weather, and energy prices. Let’s take a look at two possible scenarios:
Scenario 1: Opportunity for electric vehicles to automatically charge during off-peak hours or when renewable energy production is high, optimizing both cost and energy use. In this case, electric vehicle data analytics helps to refine charging schedules.
Scenario 2: Ability for local microgrids to temporarily disconnect from the main grid and operate independently during outages or maintenance, significantly enhancing reliability and reducing disruption.
In their turn, businesses will be able to leverage IoT-enabled smart grids to automate and optimize their energy consumption, potentially qualifying for energy credits by participating in demand response programs. Additionally, the ability to generate and sell back excess energy to the grid can open new revenue streams, aligning profitability with sustainability initiatives.
Note: Any smart grids and IoT implementation project in business requires manufacturing software development services provided by a trusted development agency.
You may also be interested in exploring how to get started with a smart factory from another blog post by Intelliarts.
Building IoT-enabled smart energy solutions with Intelliarts
Smart energy solutions are of interest to two types of businesses:
- Energy and utility companies, looking to modify their energy infrastructure and reinforce it with IoT.
- Innovative tech companies, looking to exploit their IoT devices in the energy sector.
Variations are possible, but anyway, in this scenario, we are discussing either the improvement of energy infrastructure or utilization of IoT devices related to energy management, or both.
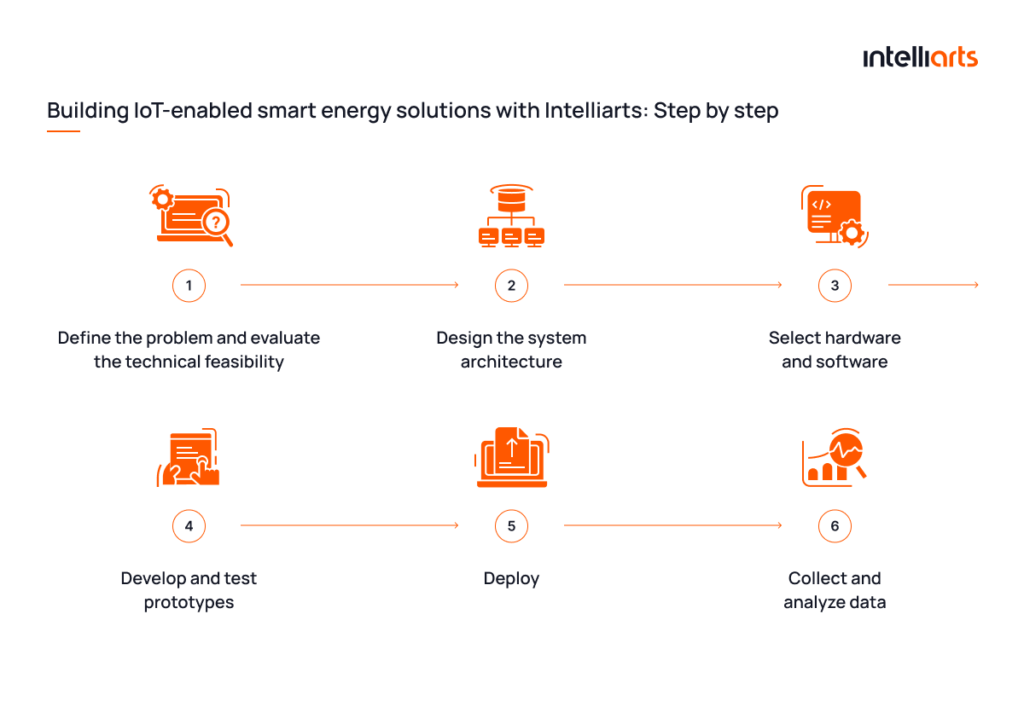
Should you need a smart energy solution for your business, you need to understand what the process for creating your software will look like. Here’s what building an IoT-enabled smart energy solution with the Intelliarts team can look like:
Step 1: Define the problem and evaluate the technical feasibility
Above everything, you should identify the specific energy-related problems that you want to solve. Here are a few examples:
- Reducing energy consumption
- Optimizing load distribution
- Enhancing renewable energy usage
- Minimizing downtimes of IoT devices or energy machinery
Once you understand what exactly will be the goal of the project, you should proceed with the technical feasibility evaluation. This includes assessing the available technology and the infrastructure needed. Basically, in this stage, you need to ensure that your team both economically and technically can fulfill the project requirements, given their appropriate expertise in this matter.
Step 2: Design the system architecture
Next, you need a basic design of the IoT system architecture, which includes
- Devices/Sensors: IoT units to monitor energy usage, temperature, light levels, etc.
- Connectivity: Communication protocols and networks (Wi-Fi, Zigbee, LoRa, etc.) to connect devices
- Data processing: Means of data aggregation, filtering, and analysis, either at the edge or in the cloud
- User interface: The way users or admins are supposed to interact with the ready system, via mobile apps, web dashboards, etc.
Explore our smart grid software development service.
Step 3: Select hardware and software
The choice of hardware boils down to manufacturing suitable ones if your company specializes in it or selecting appropriate IoT devices that are already available on the market. In the case of the latter, consider the following factors:
- Purpose of hardware
- Cost-efficiency
- Compatibility
- Reliability
- Capability to withstand expected working conditions
As for software, you’ll likely need assistance from a trusted development agency to create and integrate a tailored solution for an IoT-based smart grid.
In smart grids, software can play two roles:
- Empowering IoT devices
- Providing a solution to manage the IoT smart grid as well as gather and analyze data
Software should be both compatible with IoT devices and useful enough for users or admins of the end smart grid system.
Step 4: Develop and test prototypes
Then, it’s necessary to create initial prototypes of the software solution for the IoT device — smart grid pair, and test how they work together. Leveraging automated IoT testing solutions can greatly streamline this stage by simulating real-world conditions, reducing manual effort, and improving accuracy across diverse device and network environments. Here are some testing approaches to consider using:
- Integration testing
- Functional testing
- Performance testing
- Security testing
- User acceptance testing
Step 5: Deploy
Start with a pilot project in a controlled environment to monitor how the system performs in a live setting. This approach allows for adjusting strategies and resolving any issues before full-scale deployment. Monitoring, as well as staff training and ongoing support, are mandatory at this stage.
Step 6: Collect and analyze data
Finally, as the goal of IoT smart grids is to acquire data for further usage, it’s necessary to set the respective procedures up.
Real-time vs batch processing: Decide if the system requires real-time data processing or if batch processing is sufficient based on the needs of the application.
As for data analysis, here are some approaches you may consider using:
- Descriptive Analytics
- Predictive Analytics
- Prescriptive Analytics
Additionally, it’s recommended to incorporate a feedback mechanism to continuously improve the system. Use the insights gained from data analysis to refine the deployment, enhance system performance, and better meet user needs.
Final Take
IoT applications in smart grid significantly upgrade traditional power systems by improving efficiency, reliability, and consumer interaction. As smart grids evolve with IoT integration, they promise automated energy adjustments, sustainable practices, and greater consumer participation, offering businesses operational efficiencies and new revenue opportunities. This makes smart grid technology a strategic investment for future-focused companies.
Consider partnering with a trusted development agency should you need an IoT-based smart grid solution. Here at Intelliarts, we’ve been on the market for more than 24 years, delivering software for businesses from across various industries like renewable energy software development. Our expert engineers can address your project needs on many levels.
FAQ
1. How does the smart grid system benefit the environment in IoT?
The smart energy grid using IoT enhances environmental sustainability by improving energy efficiency, reducing waste, and facilitating the integration of renewable energy sources, thereby decreasing carbon emissions.
2. How does IoT apply to smart energy?
IoT for smart grids enables real-time energy monitoring and management, allowing for efficient use of resources, predictive maintenance, and improved demand response capabilities in smart energy systems.
3. What are the layers of the smart grid?
The layers of a smart grid in IoT include the Perception Layer (data collection), Network Layer (data transmission), and Application Layer (data analysis and device management).












