Since infrastructure, digital assets, operational processes, and regulations evolve rapidly, IT businesses have to conduct regular IT audits. The purpose of such inspections is to assess the state of technology adopted by a company.
In this post, we delve deeper into technology audits. We learn what types and forms of audits are there, what the reasons for conducting audits are, and what the potential business value of such an intervention is. Finally, we’ll review a typical audit flow and review challenges that can interfere with the IT technical audit.
Understanding technology audits
A technology audit is a comprehensive assessment of an organization’s technological infrastructure, policies, and operations.
Technology audit involves a systematic review of IT assets, processes, and policies. The purpose is to identify strengths and weaknesses in the technology framework, uncover potential risks, and provide recommendations for improvement, which is where a tech consulting company can be invaluable. The end goal of conducting a technology audit is to ensure that the technology in use is efficient, secure, and aligned with the business’s strategic goals.
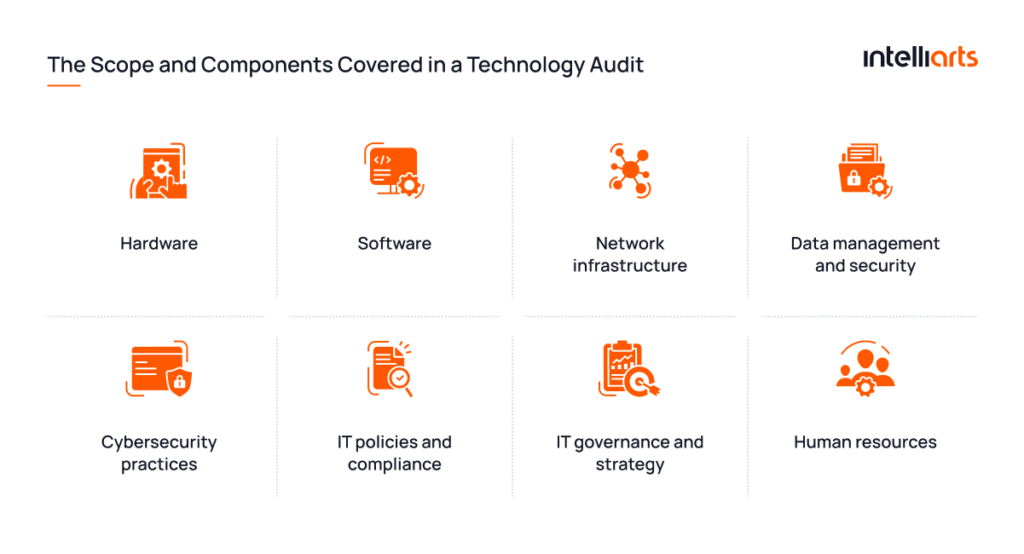
The scope and components covered in a technology audit can vary. Here are the areas that are typically examined throughout a thorough audit:
- Hardware: Examination of physical devices like servers, computers, and networking equipment to assess their performance, maintenance, and suitability for the organization’s needs.
- Software: Evaluation of software applications for licensing compliance, usage effectiveness, and security vulnerabilities.
- Network infrastructure: Assessment of the network setup, including its design, security protocols, and performance metrics.
- Data management and security: Review of how data is stored, accessed, and protected. This includes data backup systems, encryption methods, and compliance with data protection laws.
- Cybersecurity practices: Analysis of security measures such as firewalls, anti-virus software, and intrusion detection systems.
- IT policies and compliance: Review of IT policies and procedures to ensure they align with legal and industry standards.
- IT governance and strategy: Evaluation of how IT aligns with the organization’s overall strategy, including IT governance structures and decision-making processes.
- Human resources: Assessment of the IT team’s skills, training, and capacity to manage and support the technology infrastructure.
A technology audit helps to ensure operational efficiency and security and plays a crucial role in strategic planning, helping organizations make informed decisions.
Audits can be categorized by the entities involved and the main purposes. Review the general comparison in the infographic below:

Reasons for Conducting a Technology Audit
Before deepening into the rationale behind technology audit, take a look at video delivering into what IT audit is and what it takes to be an IT auditor.
Some companies, especially ones that deal with sensitive customer information, like financial institutions, typically conduct tech audits twice a year. While it is a rather periodical procedure, there are other reasons and indications that may push the management to the need to request a technical audit:
#1 Identifying vulnerabilities and risks in the technology infrastructure
A technology audit serves as a diagnostic tool, unveiling vulnerabilities within an organization’s IT infrastructure. This proactive approach is crucial in identifying weak points that could be exploited by cyber threats.
To be completely clear, an audit, especially an internal one, is not about finding flaws. It’s rather about strengthening the infrastructure behind your digital assets, detecting limitations, and identifying operational weaknesses to adapt to the ever-changing business environment.
#2 Optimizing technology investments
IT audits assess the efficiency of the current IT resources, helping to reallocate budgets and efforts to areas that offer the highest return on investment and eliminating wasteful or redundant technology spending.
IT audits are about maximizing the value per dollar spent on your business.
#3 Ensuring regulatory compliance and data security
For businesses, particularly those in highly regulated industries, compliance is not optional. Technology audits are instrumental in ensuring that the organization’s IT practices align with legal and regulatory requirements.
Ensuring compliance with regulations such as HIPPA and GDPR is especially critical for companies dealing with sensitive customer data. After all, the failure to comply with regulations may result in penalties of up to 20 million euros or up to 4% of yearly revenue. Another world’s well-known standard is ISO/IEC 27001:2022 which regulates matters of information security, cybersecurity, and privacy protection. It’s to be complied with by all organizations having an online presence and, in particular, by IT businesses.
Additionally, through audits, businesses can demonstrate their commitment to data security, a factor that significantly influences customer trust and industry credibility.
#4 Aligning technology with business goals and strategies
Audits are essential in ensuring that an organization’s IT infrastructure is not only robust but also aligned with its long-term goals and strategies. Key areas that should be aligned with business perspectives, for example, for scaling, are:
- Computational Resources
- Network Infrastructure
- Software and Applications
- Licenses
- Data management and analytics
- Cybersecurity measures
- Cloud services and solutions
- Mobility solutions
This alignment is vital for driving growth, innovation, and competitive advantage. By regularly assessing the effectiveness of technology in relation to business objectives, companies can make informed decisions that propel them forward in their respective markets.
#5 Mitigating potential threats or disruptions
Technology audits aid in identifying and mitigating potential IT threats or disruptions before they escalate. Examples include:
- Cybersecurity breaches
- Data leakage or loss
- Outdated or unsupported software and hardware
- Network downtime or failures
- Compliance violations with data protection laws
- Insider threats and employee misconduct
- Malware and ransomware attacks
- Natural disasters impacting IT infrastructure
- System overloads or performance bottlenecks
- Unsecured or inefficient cloud storage and services
This proactive approach is key to maintaining uninterrupted business operations, safeguarding data integrity, and ensuring continuity in the face of unexpected challenges.
Benefits of technology audits for businesses
As a board member, business owner, C-level executive, or another specialist involved in strategic decision-making, you should know exactly what business value such an initiative as technical inspection can bring to your business. Key advantages of information system audit are as follows:
- Enhanced data security and protection against cyber threats
- Improved productivity and streamlined processes
- Cost savings through identifying unnecessary expenses or inefficiencies
- Better decision-making through accurate technology assessment
- Competitive advantage and future-proofing the business
As a bonus point, an audit in IT can direct a company toward digital transformation or other beneficial changes in the qualification of team members, workflow processes, management approaches, and more. After all, tech inspection is not only about examining the technology but also about advancing the business operating on this technology in general.
Want to reap the most benefits of your tech infrastructure inspection? Contact Intelliarts and let our engineers, business analysts, and other specialists aid you.
How to conduct tech audit: Process steps & best practices
In general, conducting a technology audit is a series of steps for preparation, gathering information, testing, and providing recommendations. With our experience, Intelliarts can provide a flow for a typical audit of an information technology system and best practices for it:
#1 Define the scope of the audit
This step involves outlining the boundaries and focus areas of the audit. It sets the stage for what needs to be examined and evaluated. It includes:
- Determining which technologies and systems to review
- Establishing the goals and objectives of the audit
- Identifying key areas of focus, such as security, compliance, and efficiency
Best practices for execution: The scope should be clearly defined and aligned with the organization’s strategic goals. It’s important to ensure the scope is realistic and manageable.
#2 Identify the stakeholders
Next, you should identify all parties who have an interest in the audit’s outcome. These could be internal or external to the organization. Possible actions here are:
- Listing individuals and departments affected by the audit
- Determining who will provide input and who will use the audit results
Best practices for execution: Engage stakeholders early and ensure their involvement throughout the process for better acceptance and support.
#3 Gather information
This step implies collecting relevant data and information about the current state of technology in the organization. It includes:
- Reviewing documentation, systems, and processes
- Conducting interviews and surveys
- Analyzing existing data and reports
Best practices for execution: Use a variety of data collection methods and ensure the information is accurate and comprehensive.
#4 Run tests
It implies conducting practical tests on the IT systems to evaluate their performance and security under various scenarios and compliance with both regulations and internal documentation. Tests may include:
- Comparing data against best practices and benchmarks
- Identifying gaps and inefficiencies
- Assessing risk and compliance issues
- Ensuring the match between factual processes and processes detailed in documentation
Best practices for execution: Ensure tests are thorough, cover all critical areas, and use industry-standard testing methodologies. You can use performance testing tools like LoadRunner, security testing tools like Nessus, Compliance testing tools like Qualys, etc. Document all findings for analysis.
#5 Analyze the data
This step involves examining the gathered information to identify trends, issues, and areas for improvement. Recommended actions here are:
- Comparing data against best practices and benchmarks
- Identifying gaps and inefficiencies
- Assessing risk and compliance issues
Best practices for execution: Use both qualitative and quantitative analysis methods and keep the analysis objective and data-driven.
#6 Develop recommendations
In this step, auditors develop suggestions for improving technology systems based on the results they obtained in previous steps, which include:
- Proposing solutions for issues identified
- Enhancing technology efficiency and security
- Recommending policy changes
Best practices for execution: Make actionable, realistic recommendations aligned with strategic objectives. Point out all limitations and weak points and suggest short-term and long-term ways to fix them in case the weaknesses cannot be addressed immediately.
#7 Prioritize recommendations
This step involves systematically deciding which recommendations from the audit should be implemented first. Possible actions here are:
- Evaluating the impact, feasibility, and cost of each recommendation
- Identifying quick wins and strategic changes
Best practices for execution: It’s essential to engage key stakeholders in this process to ensure buy-in and a realistic assessment of the organization’s capacity to implement changes.
#8 Develop an action plan
This step is about translating the prioritized recommendations into a tangible and structured action plan. It is guided by priorities set in the previous step and defines how and when the recommendations will be implemented. Possible suggestions for you here are:
- Setting timelines and milestones
- Assigning responsibilities and resources
Best practices for execution: The action plan should be detailed yet flexible, allowing for adjustments as needed. It’s important to communicate the plan clearly to everyone involved and ensure there is accountability for each aspect of the implementation.
#9 Monitor progress
Monitoring involves regularly reviewing the implementation of the action plan to ensure it is on track and achieving its intended goals, which includes:
- Tracking progress against the plan
- Adjusting the plan based on feedback and results
Best practices for execution: Effective monitoring requires setting up clear KPIs to measure progress. It’s also important to maintain open communication channels for feedback.
You can review one of the typical IT technical audit examples in the image below or download the Technical Audit Checklist PDF version.
It’s important to understand that the checklist provides basic items and a common approach to structuring them.
Before IT auditing, you must determine the exact aspects to be examined and come up with exact criteria for assessment. You also should preplan tests, such as testing the false password proofing, checking the process for managing alerts, and more.
Additionally, you can consider using AI-driven tools to facilitate the IT audit process. For example, generative AI may be used for business process document summarization, while other AI-driven solutions can aid in test result analysis.
For thorough testing, you may need the assistance of a trusted provider of software development services, which can examine the system on a deeper technological level.
Should you need any help with a technology audit, particularly of AI-based apps, platforms, and other software solutions — don’t hesitate to contact Intelliarts.
Challenges of IT audits
Auditing technology information systems can be daunting, especially in more well-established organizations with a large part of legacy infrastructure, bureaucracy, or obsolete processes. Key difficulties that can arise during an IT technical audit include:
- Ensuring compliance with the regulatory environment
- Managing unorganized data within the organization
- Communication difficulties
- Choosing and conducting tests that can help examine technology
- A mismatch between factual and documented information about processes or components
- Balancing the need for thorough auditing with limited resources and time constraints
- Addressing the resistance to change and cooperation issues within the organization
An interesting aspect here is that the very resistance of the team and the technical difficulties in conducting an audit are negative indicators by themselves. It’s indeed rare when a company without well-built processes, clean code in core components of software, or solid communication practices can perform on a high level based on typical AI audit metrics.
Final Take
The importance of information technology auditing is hard to overestimate. It helps identify areas for improvement, aids in staying compliant with regulatory requirements, and provides perspectives on how to reinforce the products, infrastructure, and processes in the company.
While some forms of information technology & system audits can be conducted in-house, for the best results and professional view, it’s recommended to apply for external audits with some periodicity. Request tech audit from Intelliarts, a trusted provider of AI/ ML development and technology consulting, as well as other IT services. With more than 24 years on the market, we can direct your company in the right direction.
FAQ
1. How long does a technology audit typically take?
Typically, a technology audit takes between a few weeks to several months, depending on the business’s size and the complexity of its IT infrastructure.
2. Will a technology audit disrupt my business operations?
A well-planned technology audit minimizes disruption, often conducted with little to no impact on daily business operations.
3. What are the costs associated with a technology audit?
Costs vary widely based on the audit’s scope and company size but can range from a few thousand to tens of thousands of dollars.