Solution Highlights
- Developed an ML-based early warning system predicting respiratory exacerbations
- Processed 150,000+ sensor records per night into 360 daily features per patient
- Accurately identified most respiratory risk cases while minimizing false alerts in clinical settings
- Advanced the solution from research to clinical pilots with 50+ patients in 18 months
About the Project
Customer:
Our partner (under NDA) is a healthcare technology company developing contactless patient monitoring solutions. The company designs smart, sensor-based systems embedded into everyday sleep environments, such as beds and mattresses, to continuously collect physiological data. By leveraging advanced analytics and machine learning, the platform detects early signs of respiratory deterioration, breathing exacerbations in particular, and help intervene before conditions escalate.
Challenges & Project Goals:
The project initially started as a research initiative focused to find out whether the sensor data collected from contactless patient monitoring could reliably support predictive analytics. The customer contacted Intelliarts to assess data quality, structure heterogeneous time-series signals, and validate the feasibility of applying machine learning (ML) to this data.
After proving that meaningful predictions could be derived from patient measurements, the project evolved toward a more advanced objective. Our team was asked to build an ML model for detecting early signs of respiratory exacerbations.
Solution:
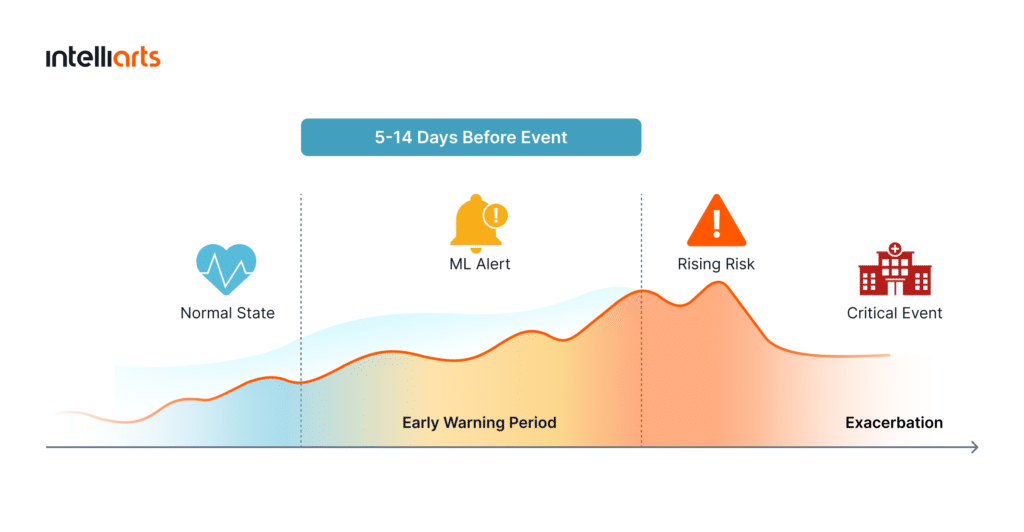
Intelliarts developed an ML–based early warning system for respiratory exacerbations. It analyzes daily physiological signals per patient and identifies patterns that indicate an increased risk of breathing complications. The idea is to provide clinicians with advance warnings, from 5 to 14 days ahead, before symptoms become critical.
The system is built on classical ML models optimized for time-series classification and scoring.
Business Value Delivered:
The Intelliarts team delivered an ML solution that created tangible business and clinical value by:
- Validating the feasibility of predictive analytics for contactless patient monitoring
- Enabling early detection of exacerbations to support preventive clinical care
- Reducing reliance on reactive emergency interventions through advance risk alerts
- Demonstrating real-world ML performance to investors and clinical stakeholders
- Providing a scalable foundation for hospital deployment and market expansion
ML Development, Data Analysis, Cloud Services, Big Data, Business Intelligence & Analytics, Data Science
Technology Solution
The Intelliarts team built an end-to-end ML solution that converts high-volume sensor data into clinically meaningful insights to enable preventive medical intervention for breathing exacerbations rather than reactive emergency care.
Here’s how the solution was implemented step by step:
Step 1: Data exploration and labeling strategy
We started by analyzing the available sensor data and patient population to define what constitutes a respiratory exacerbation. At this stage, we also identified a major technical challenge with the customer’s SQL database. While the database reliably stored large volumes of sensor data, it was not optimized for analytical workloads. The lack of proper indexing and normalization meant that data extraction took us hours.
So the first step was to optimize the database structure and indexing strategy and reduce data retrieval times to minutes. Since direct clinical labels were not available, our ML engineer designed a proxy labeling approach based on medication intake.
Using historical records from the database, we then identified exacerbation events by detecting consecutive days of prescribed antibiotic usage, indicating physician-confirmed respiratory complications.
Step 2: Time-series aggregation and feature engineering
Each patient generated up to 150,000 sensor records per night, resulting in more than 58 million data points annually per patient. At the same time, labels existed only at the daily level, which made raw data unsuitable for direct modeling.
To solve this, we aggregated high-frequency time-series signals into meaningful daily features. By and large, a major part of this project focused on feature engineering. Specifically, our ML team transformed raw signals into statistically meaningful indicators, such as Z-score–based deviations from individual patient baselines, moving averages, lag features, and sleep behavior metrics (e.g., nighttime pattern changes and awakenings).

Z-score deviation over time, showing increasing anomaly as respiratory exacerbation develops
This process helped us reduce tens of millions of annual records into approximately 360–370 daily records per patient suitable for ML training.
Step 3: Baseline modeling and ML development
The first predictive model relied purely on statistical features derived from Z-scores to prove feasibility. Once validated, we expanded the feature set and trained classical ML models, starting with logistic regression and later moving to gradient boosting algorithms (XGBoost) to improve performance on complex temporal patterns.

ML model predictions highlighting elevated exacerbation risk from 10 to 4 days before onset
Step 4: Validation and clinical alignment
One more challenge of this ML project was the limited number of patients, only 20, which significantly impacted model training and validation and increased the risk of overfitting. Therefore, we decided to apply advanced validation techniques, including leave-one-patient-out and cross-validation.
Also, model outputs were continuously analyzed to confirm clinical plausibility. Based on the results, our ML engineer performed data cleaning and logic refinement when he noticed that sensor artifacts or behavioral changes distorted predictions.
Throughout this process, the team also consulted with medical experts to align model behavior with real-world clinical expectations.
Step 5: Performance optimization
In a healthcare context, model performance must be evaluated beyond overall accuracy. Our team focused on sensitivity and specificity as two critical metrics for medical risk prediction.
Sensitivity (also known as recall) measures how well the model identifies true exacerbation cases, while specificity reflects how accurately it avoids false alarms. These metrics are inherently interdependent: increasing sensitivity often reduces specificity, and vice versa.
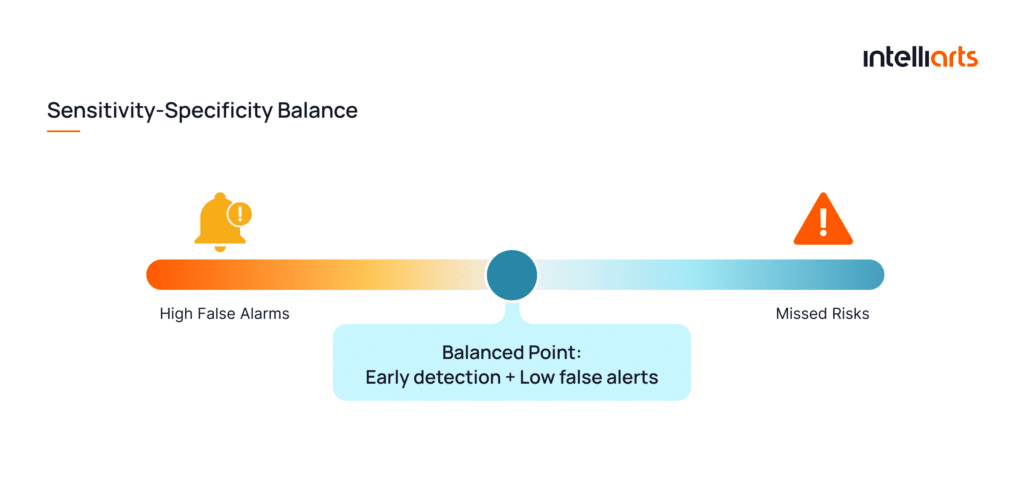
The goal was to achieve high sensitivity while maintaining at least 90–95% specificity. This could ensure early detection without overwhelming clinicians with false positives. By the end of the project, the model reached approximately 80% sensitivity at 95% specificity, which demonstrated its strong early-warning capability.
Business Outcomes
Our ML team delivered a clinically viable ML solution for early detection of respiratory exacerbations. No doubt the solution creates long-term value for both healthcare providers and patients:
- Earlier clinical intervention, reducing the likelihood of emergency hospitalizations
- Improved patient outcomes through proactive, preventive care
- Lower operational burden on healthcare staff by minimizing false alarms
- Scalable clinical monitoring, supporting broader hospital and cross-market adoption
With strong sensitivity and specificity results, the ML solution also proved its predictive capability in controlled clinical environments.
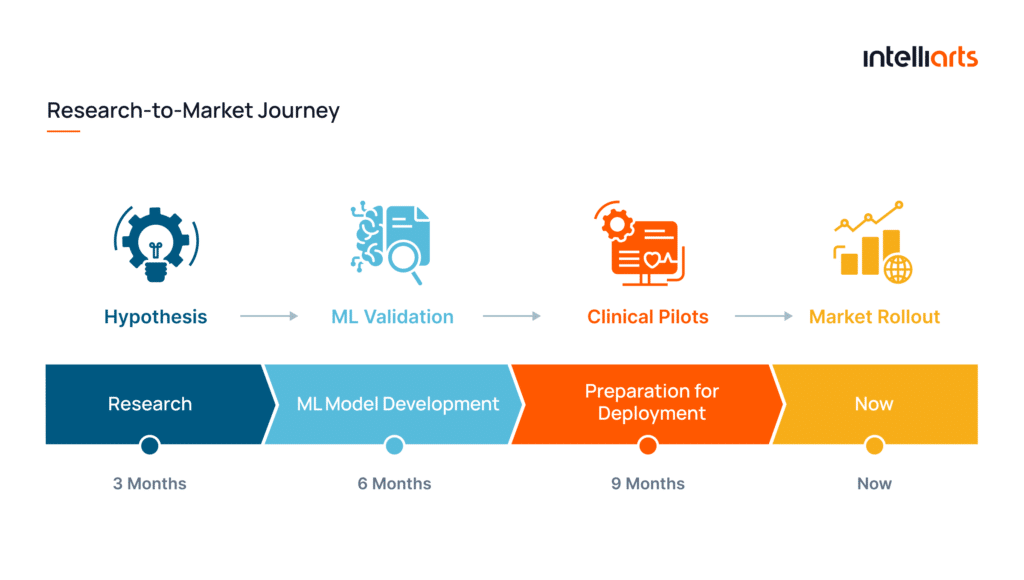
What’s more, we helped the customer move from an initial research hypothesis to a market-ready product. Within only one year, the team validated feasibility and demonstrated real-world performance to investors. In approximately 18 months, the solution evolved into a clinically tested system. It was presented at an international conference, prepared for patenting, and piloted with 50+ patients in hospital settings, with plans to expand into the U.S. healthcare market.














