By 2034, the revenue of AI in the agriculture market is expected to reach $12.47 billion, with each AI segment showing increased revenues. Agriculture technology-as-a-service is already an entirely new, prosperous market, and the adoption of AI in this domain is growing overall. In that regard, what applications of AI should agriculture companies prioritize, and how should they approach high-tech development?
In this post, you’ll explore the value-adding benefits of using AI in agriculture, examples of real-life AI applications in agriculture. Moreover, you’ll explore providers of corresponding software solutions in the industry. Besides, you’ll explore artificial intelligence in agriculture challenges and find out about three high-tech implementations of this technology that await humanity in the near future.
Benefits of AI in agriculture: The top advantages you should consider
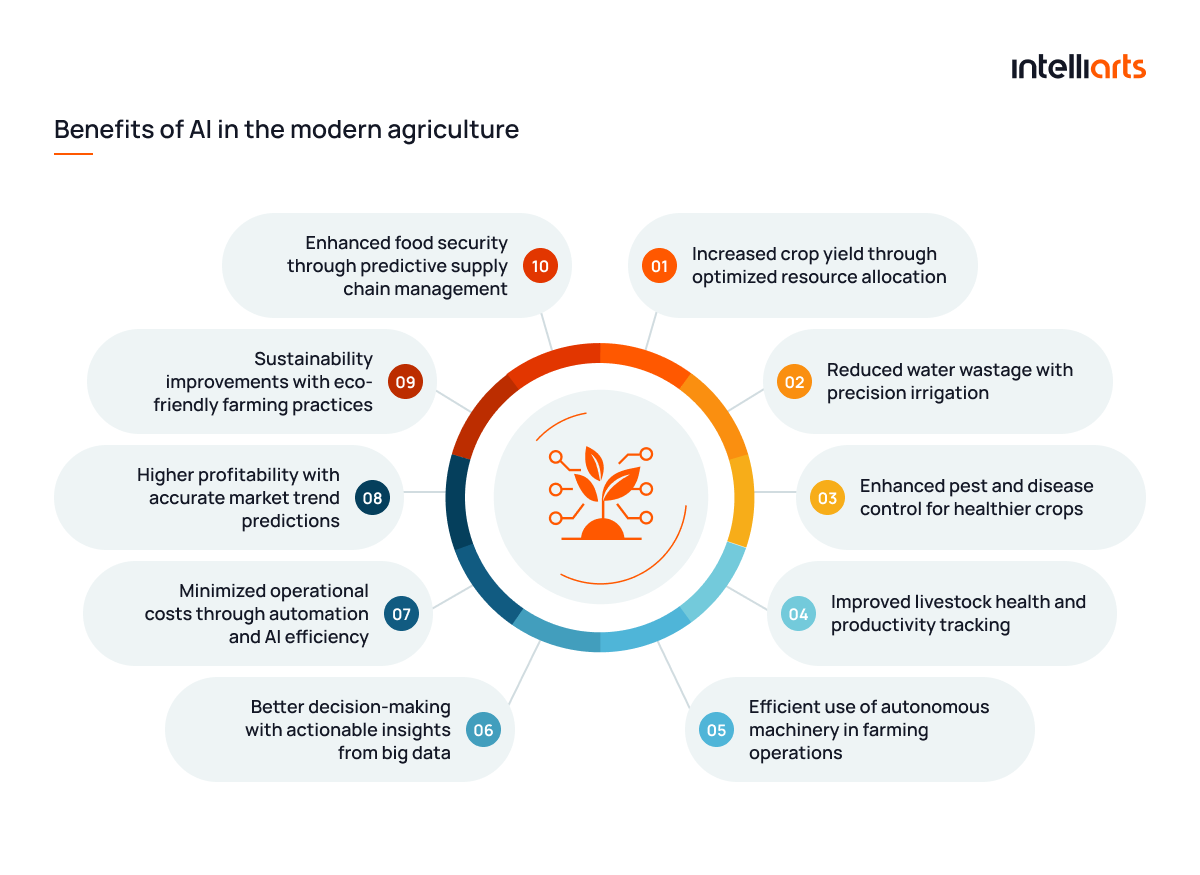
Before we proceed with exploring applications of AI in farming and adjacent sectors, let’s take a look at the benefits that the usage of AI have already shown:
- Increased crop yield through optimized resource allocation: AI can help analyze soil fertility, weather patterns, and crop requirements. This allows farmers to use resources like water, fertilizers, and nutrients more efficiently. One of the key benefits of AI in farming is boosting yield without increasing land use.
- Reduced water wastage with precision irrigation: Monitoring soil moisture and weather forecasts with AI enables farmers to use just the right amount of water. Respectively, businesses do not only conserve water but improve soil health, which proves the key benefits of using AI for soil health analysis in sustainable agriculture.
- Enhanced pest and disease control for healthier crops: Computer vision paired with machine learning are able to detect early signs of crop stress, pests, or disease. As a result, farmers can provide timely treatment.
- Improved livestock health and productivity tracking: With AI systems, farmers and businesses monitor animal behavior, feeding patterns, etc. in real time. They detect health issues early if any and can then improve feed plans and routine across the herd.
- Efficient use of autonomous machinery in farming operations: A good solution to reduce labor costs is to use self-driving tractors, drones, and harvesters powered by AI. These can work around the clock, provide real-time data collection, bring more precision. Thus, this automation represents the most noticeable benefits of AI in agribusiness, especially for large-scale farms.
- Better decision-making with actionable insights from big data: From satellite imagery to sensor data, AI processes large datasets to be able to deliver real-time recommendations for planting, harvesting, and crop rotation. In this long run, companies benefit from smarter, more strategic decisions at every stage of the farming cycle.
- Minimized operational costs through automation and AI efficiency: Like in other fields, AI brings automation to agriculture, for example, by speeding up weeding, spraying, or crop monitoring. The result? Lower labor costs and higher productivity.
- Higher profitability with accurate market trend predictions: AI in agriculture also contributes to smarter financial outcomes. It helps to predict commodity prices, demand fluctuations, and buyer behavior so farmers can choose better timing for sales and supply planning.
- Sustainability improvements with eco-friendly farming practices: From reducing chemical use and carbon footprint to promoting regenerative practices, AI supports sustainable agriculture. For example, the use of AI for soil monitoring and crop planning helps farmers build healthier ecosystems.
- Enhanced food security through predictive supply chain management: AI also supports global food resilience by predicting disruptions, logistic optimization, and reduced food waste.
You may explore how agriculture software development by Intelliarts reshapes your business operations and assists in other ways from our corresponding service page.
How is AI used in the agriculture sector?
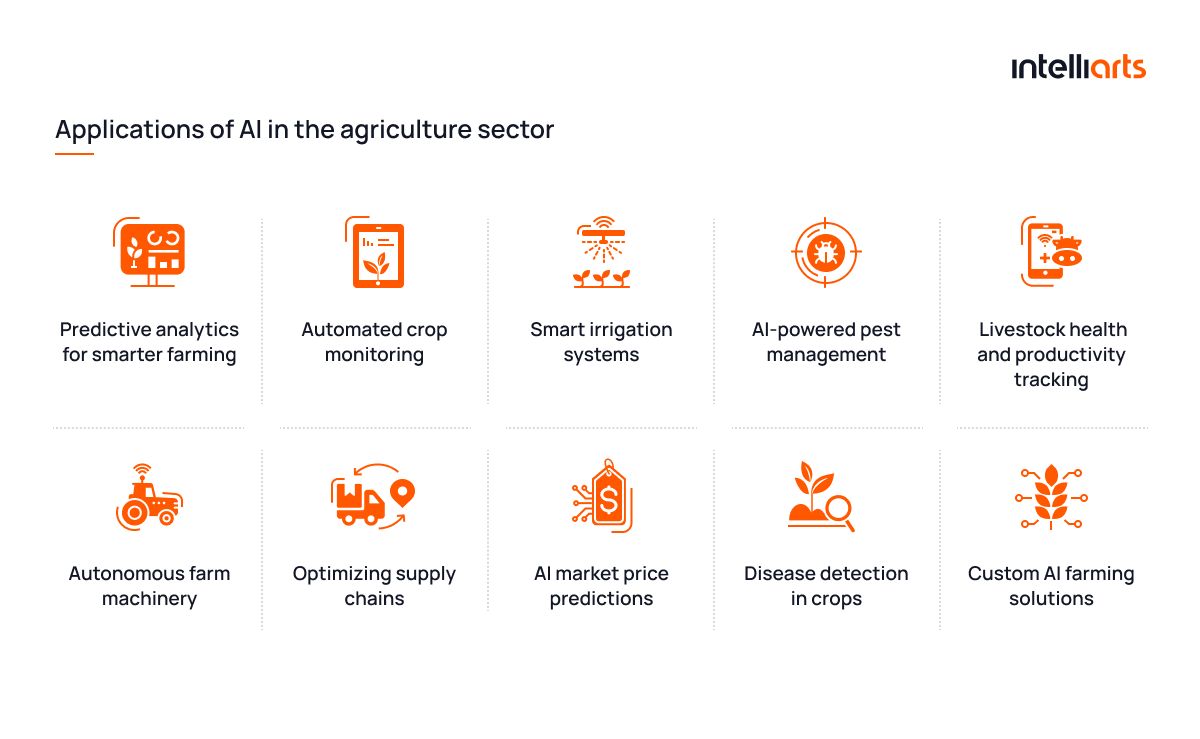
The usage of AI revolves around capabilities such as image processing, data processing, and text and imagery generation. Altogether, it derives into a range of specialized applications of AI for farming. The list includes:
#1 Predictive analytics for smarter farming
AI analyzes historical and real-time data, such as weather patterns, soil conditions, and wheat growth, to provide farmers with actionable insights. Researchers on predictive models show the high potential impact of optimizing planting schedules, forecasting yields, and anticipating challenges like pest infestations or extreme weather. As such, forecasting of planting dates and fertilizer application rates can achieve a 15% increase in average yields over three growing seasons.
Examples:
- Yield forecasting to predict harvest quantities.
- Soil nutrient mapping for precise fertilization.
- Predicting pest outbreaks based on weather and crop conditions.
- Identifying optimal planting and harvesting windows.
- Anticipating drought or flood risks for mitigation planning.
Providers:
Intelliarts, John Deere, IBM Watson Agriculture, Corteva Agriscience, BASF Xarvio, Syngenta Cropwise
There’s a range of AI models available on the market. Most of them can analyze data. Explore whether Claude AI or ChatGPT for your business can be proven to be a perfect fit for smarter farming, among other applications.
#2 Automated AI-powered crop monitoring
AI-powered sensors and drones use computer vision to monitor crop health, detect growth anomalies, and identify issues such as nutrient deficiencies or pests. This helps farmers make timely decisions and reduce losses.
Examples:
- Drone-based imaging for spotting pest infestations early.
- Monitoring growth patterns and detecting underperforming areas.
- Identifying nutrient deficiencies in specific crop sections.
- Mapping fields to analyze irrigation effectiveness.
- Spotting weed growth for targeted removal.
Providers:
Intelliarts, PrecisionHawk, Climate FieldView, Sentera, AgEagle, SlantRange
Automated crop monitoring largely depends on computer vision technology. Explore AI and computer vision in the corresponding post by Intelliarts.
#3 Smart irrigation systems
AI-enabled systems analyze weather data, soil moisture levels, and plant requirements to automate water distribution. These systems are particularly useful in drought-prone areas and play a key role in conservation of water resources in modern farming.
Examples:
- Automated drip irrigation systems based on soil moisture levels.
- Smart sprinklers adjusting to real-time weather updates.
- Water usage optimization to prevent over-irrigation.
- Tailored irrigation schedules for crop-specific needs.
- Detecting and addressing water leaks in irrigation networks.
Providers:
Netafim, CropX, Valmont Industries, Lindsay Corporation
#4 AI-powered pest management
AI models analyze pest behavior and environmental conditions to predict outbreaks and recommend mitigation strategies. Drones and cameras identify infestations early, allowing targeted pesticide applications.
Examples:
- Using drones to map pest hotspots for targeted spraying.
- Predicting pest migration patterns based on weather data.
- Early identification of pest larvae for intervention.
- Reducing pesticide overuse by applying it only in affected zones.
- Tracking and analyzing pest resistance trends over time.
Providers:
Taranis, AgriSense, Pessl Instruments, Bayer Digital Pest Management
#5 Livestock health and productivity tracking
AI monitors livestock health and behavior using sensors, cameras, and wearables. It detects early signs of illness, monitors activity levels, and optimizes feeding schedules to positively impact productivity and animal welfare.
Examples:
- Monitoring cattle temperature to detect fever early.
- Tracking activity levels to identify breeding windows.
- Detecting irregular eating patterns indicative of illness.
- Optimizing feed distribution for weight gain and milk production.
- Analyzing herd movement to detect stress or overcrowding.
Providers:
Intelliarts, Cargill, Connecterra, Allflex Livestock Intelligence, HerdDogg, SCR Dairy
#6 Autonomous farm machinery
AI-powered autonomous tractors, harvesters, and sprayers handle tasks like plowing, planting, and harvesting with minimal human intervention. These machines use GPS and sensor data to optimize operations and reduce waste.
Examples:
- Autonomous tractors for precision plowing and planting.
- GPS-guided harvesters for minimal crop damage.
- AI-powered drones for crop spraying.
- Weed-removal robots for targeted herbicide application.
- Self-driving machinery for transporting produce.
Providers:
John Deere, CNH Industrial, Kubota Smart Agriculture, Raven Autonomy
#7 Optimizing supply chains
AI improves efficiency in agricultural supply chains by predicting demand, optimizing logistics, and ensuring timely delivery of produce. It minimizes food waste and reduces operational costs.
Examples:
- Real-time inventory management for perishable goods.
- Predicting market demand for crop planning.
- Route optimization for faster produce delivery.
- Detecting and mitigating supply chain bottlenecks.
- Automating quality checks during transport and storage.
Providers:
Intelliarts. IBM Food Trust, FBN, SAP Agriculture, Tive, Trimble Agriculture
#8 AI market price predictions
AI analyzes market trends, weather data, and global trade patterns to predict crop prices. This allows to make informed selling decisions which offers to mitigate risks and enhance profitability.
Examples:
- Predicting crop price fluctuations based on weather forecasts.
- Analyzing market demand trends for optimal selling times.
- Assessing the impact of global trade policies on pricing.
- Identifying high-demand markets for specific produce.
- Evaluating the profitability of crop diversification.
Providers:
Intelliarts, Gro Intelligence, FarmLogs, Agricultural Market Information System (AMIS), Geora, Kynetec
#9 Disease detection in crops
AI leverages image recognition, drones, and sensors to identify diseases in crops at early stages. By analyzing patterns and symptoms, it helps farmers take timely action to minimize yield loss and prevent spread. It also works in the case of automated land sampling, as revealed in a corresponding success story by Intelliarts.
Examples:
- Detecting fungal infections on leaves using drone imagery.
- Identifying bacterial diseases based on crop discoloration patterns.
- Monitoring soil-borne pathogens with in-field sensors.
- Analyzing weather and humidity to predict disease outbreaks.
- Recognizing pest-related damage in crops.
Providers:
Plantix, Taranis, Scouting AI by Xarvio, Skycision
Explore AI and big data case studies by Intelliarts to find out whether we should become your trusted agritech partner for an AI in agriculture project.
#10 Custom AI farming solutions
Custom AI solutions for agriculture are tailored to specific farm needs, integrating tools like sensors, software, and analytics to address unique challenges, enhance productivity, and maximize efficiency across operations.
Examples:
- AI-driven soil testing tailored to crop requirements.
- Personalized irrigation schedules based on farm size and soil type.
- Custom algorithms for organic farming pest control.
- Specific AI tools for hydroponic or vertical farming optimization.
- Bespoke farm management platforms and dashboards for small-scale farmers.
Providers:
Intelliarts, Prospera, AgriWebb,FarmLogs, OneSoil, FarmWise
AI for agriculture: Development challenges & considerations
Let’s proceed with revealing common AI for farming and agriculture development challenges:
- Integration with existing systems. Implementing AI often requires compatibility with legacy infrastructure, such as outdated machinery or siloed software systems. Ensuring seamless integration can demand significant customization and technical expertise.
- Data quality and accessibility issues. AI relies on accurate and abundant data. Many farms face challenges in collecting reliable data due to outdated equipment, lack of IoT devices, or inconsistencies in data entry.
- Upfront cost considerations. The high initial investment for AI tools, infrastructure, and training can be a deterrent, particularly for small and medium-sized farms with limited budgets.
- Connectivity challenges in rural areas. Many agricultural regions and countries lack reliable internet or cellular coverage, which limits the deployment of AI solutions for agriculture dependent on cloud computing or real-time data transmission.
- Workforce readiness and skill gaps. Farmers and workers may lack the technical skills to operate or maintain AI systems, requiring training programs and ongoing support.
Still, even the listed challenges should not prevent you from getting started with your AI in agriculture project. Some difficulties are imminent, regardless of the project. However, they can totally be addressed through solid planning and flawless technical execution before they can actually hurt productivity or investment returns.
Here are several tips on starting with AI in agriculture from Intelliarts experts:
- Partner with experienced AI developers for smooth adoption. Collaborate with experts to customize solutions that align with your farm’s specific needs and existing infrastructure.
- Start small with modular AI tools to scale progressively. Test AI on one aspect of your operations (e.g., irrigation or pest management) before rolling out full-scale implementation.
- Invest in IoT devices and sensors to improve data quality. Reliable hardware ensures accurate and actionable insights for your AI systems.
- Provide training programs for farmers and staff. Equip workers with the skills to understand, operate, and benefit from AI-driven technologies.
Addressing technical challenges in innovative tech development requires substantial experience and expertise in software engineering.
The future of artificial intelligence in agriculture today
Finally, we’ve reached the review of AI future trends in agriculture. Although the applications listed above may sound quite futuristic already, there’s a range of even more innovative, experiment-level directions in which AI is predicted to develop. They are the following:
- Generative AI for crop improvement: Generative AI is being used to identify ideal genetic traits for breeding crops with improved yield, disease resistance, and adaptability to climate change. By analyzing large genomic datasets, AI can speed up the development of resilient crop varieties tailored to specific regions.
- AI-driven regenerative agriculture. AI technologies can help farmers transition to regenerative practices by providing real-time soil analysis and crop rotation recommendations. Besides, AI systems may monitor environmental health and offer strategies to reduce inputs like synthetic fertilizers.
- Vertical farming automation with AI. AI sensors can optimize water usage, nutrient delivery, and light exposure to maximize crop yields in limited spaces. This allows indoor vertical farms to operate more sustainably while reducing food miles in urban areas.
- Generative AI. Large Language Models (LLMs) such as GPT or Claude can help analyze agronomic reports, weather data, and sensor inputs to deliver quick insights and recommendations to farmers or agronomists. For instance, through GPT development, agribusinesses can build an advisory system for identification of optimal sowing dates and suggestion of crop protection measures.
Discover more about using AI in vertical farming, AI-driven nutrient management, and monitoring crops in the video below:
The future of AI can significantly impact businesses, individual consumers, and broader society. Explore custom ML solutions additionally to obtain a more complete picture of how innovative technologies can boost your company.
Read also about AI-driven vehicle damage assessment.
Final take
AI for agriculture shows strong potential to reinforce traditional processes and practices with innovative technologies. Predictive analytics, automated AI-powered crop monitoring, smart irrigation systems, AI for farm management, and livestock productivity tracking are only a small portion of what AI can offer agriculture and farming businesses. However, it’s important to be aware of technical challenges and upfront costs of implementing AI in agriculture.
Should you need assistance with AI in farming and agriculture development, don’t hesitate to reach out to Intelliarts — a custom ML solutions provider. With more than 24 years of experience on the market, delivering on-demand solutions to businesses from across many industries, including agriculture, we can help you reinforce your business capabilities through innovative technology.
FAQ
1. What is the cost of implementing AI in agriculture?
The cost of AI in farming depends on the tools and scale, ranging from $5,000 for basic systems to over $100,000 for advanced setups. Factors include sensors, drones, software, and training. AI farming technology is becoming more affordable with tailored solutions for different farm sizes.
2. Is AI suitable for small-scale farmers?
Yes, AI for farmers can benefit small-scale farms with affordable tools like crop monitoring apps and low-cost sensors. These AI applications in agriculture optimize water usage, predict pests, and improve yields, making artificial intelligence in farming accessible for all scales.
3. How does AI improve profitability?
AI in agriculture enhances profitability by increasing crop yields, reducing waste, and optimizing resource usage. With AI farming technology, farmers save on inputs like water and fertilizer, predict market trends, and reduce losses due to pests and diseases, boosting overall efficiency.












