Modern agriculture tends to shift toward smarter and more efficient production as environmental limits and market pressures grow. Farmers now face the challenge of maintaining productivity while using fewer resources and protecting soil and water quality at the same time. According to a 2024 McKinsey & Company survey, 61% of farmers already use digital agronomy tools, and 51% rely on precision hardware. That clearly indicates that technology-driven sustainability is becoming a practical solution, not a distant goal.
In this post, you’ll find out about core benefits of sustainable agriculture, including its economic, social, and environmental impacts. You’ll also discover about physical and software technology supporting sustainable farming, review the limitations of this approach, and learn how to balance pros and cons.
What is sustainable farming?
Sustainable agriculture is a holistic approach to food production that is intended to help meet current needs while preserving resources for future generations.
Sustainable farming, by default, integrates environmental stewardship, economic viability, and social responsibility into every decision, such as seed selection or harvest.
Unlike conventional methods that prioritize immediate yields, sustainable agriculture builds long-term resilience. It recognizes that healthy soil, clean water, and thriving ecosystems aren’t obstacles to productivity. They’re the foundation of it. Now that you know the answer to the question: “what is sustainable agriculture,” let’s proceed by reviewing the key principles of this concept.
Key principles of sustainable farming
The advantages of sustainable agriculture emerge from a framework of interconnected principles that guide farming operations. These fundamental concepts work together to create systems that are both productive and regenerative. The Intelliarts team strongly suggests reviewing these principles to understand sustainable agriculture advantages and the future of food production:
- Resource efficiency. This principle focuses on minimizing waste of water, energy, and inputs while maximizing productivity. These advantages are achieved through precision management and smart technology that targets specific field conditions.
- Soil health management. Soil management here includes building organic matter to protect soil structure. It also suggests fostering beneficial microorganisms that naturally enhance fertility and crop resilience over multiple growing seasons.
- Biodiversity enhancement. Biodiversity strategy involves supporting diverse plant and animal life both in fields and at their margins. This also includes natural pest control and pollination systems that reduce dependence on chemical interventions.
- Emission reduction. This principle encompasses decreasing greenhouse gas releases through carbon sequestration in soil, reduced tillage practices, and optimized input use. Such an approach can notably lower the carbon footprint of farm operations.
- Water conservation. Conservation strategy emphasizes implementing efficient irrigation systems. It also leverages practices that protect both water quantity and quality, since both these parameters are important for agricultural and community needs.
Explore more about farm equipment imaging in modern agricultural businesses.
Comparing farming approaches
The benefits of sustainable agriculture become clearer when contrasted with traditional methods. The differences between these approaches reveal not just alternative techniques, but fundamentally different philosophies about agriculture’s relationship with natural systems. Find the detailed comparison in the table below:
The role of technology in sustainable agriculture
Why is sustainable agriculture important in the digital age? Years ago, humanity simply didn’t have the means to sustain some of the most important sustainable farming practices as we understand them now. Luckily, modern farming technology is already capable of turning sustainability from an idea into everyday practice.
Sustainability means producing wisely, not less. The future of farming depends on a balance between growth and care for the land. — Marta Kufalska, Agritech Solution Expert at Intelliarts
Where modern technology is applied to sustainable farming:
- GPS guidance: Optimizes planting patterns and machinery paths.
- Soil sensors: Track real-time moisture, pH, and nutrient levels.
- Satellite imagery: Identifies crop stress, pest zones, and growth variations.
- Drones: Capture aerial images to monitor fields and spot issues early.
- Automated machinery: Handles planting, weeding, and harvesting with precision.
- Drip irrigation systems: Deliver water directly to roots, reducing waste and evaporation.
- Solar-powered pumps: Provide clean, renewable energy for irrigation and livestock watering.
- Smart greenhouses: Control temperature, humidity, and CO₂ levels to optimize growth.
- Composters and bio-digesters: Turn organic waste into natural fertilizer or biogas.
- Water filtration and recycling units: Reuse runoff and rainwater for irrigation.
- Vertical farming systems: Maximize space and minimize resource use in controlled environments.
Does 260% higher operational scaling sound like promising results to you? Intelliarts knows how to achieve such results with centralized sensor management software for agtech businesses.
Explore the sensor inventory management system success story by Intelliarts for more information on potential technology solutions in agriculture.
The next sections will delve deeper into how these innovations bring tangible sustainable agriculture benefits.
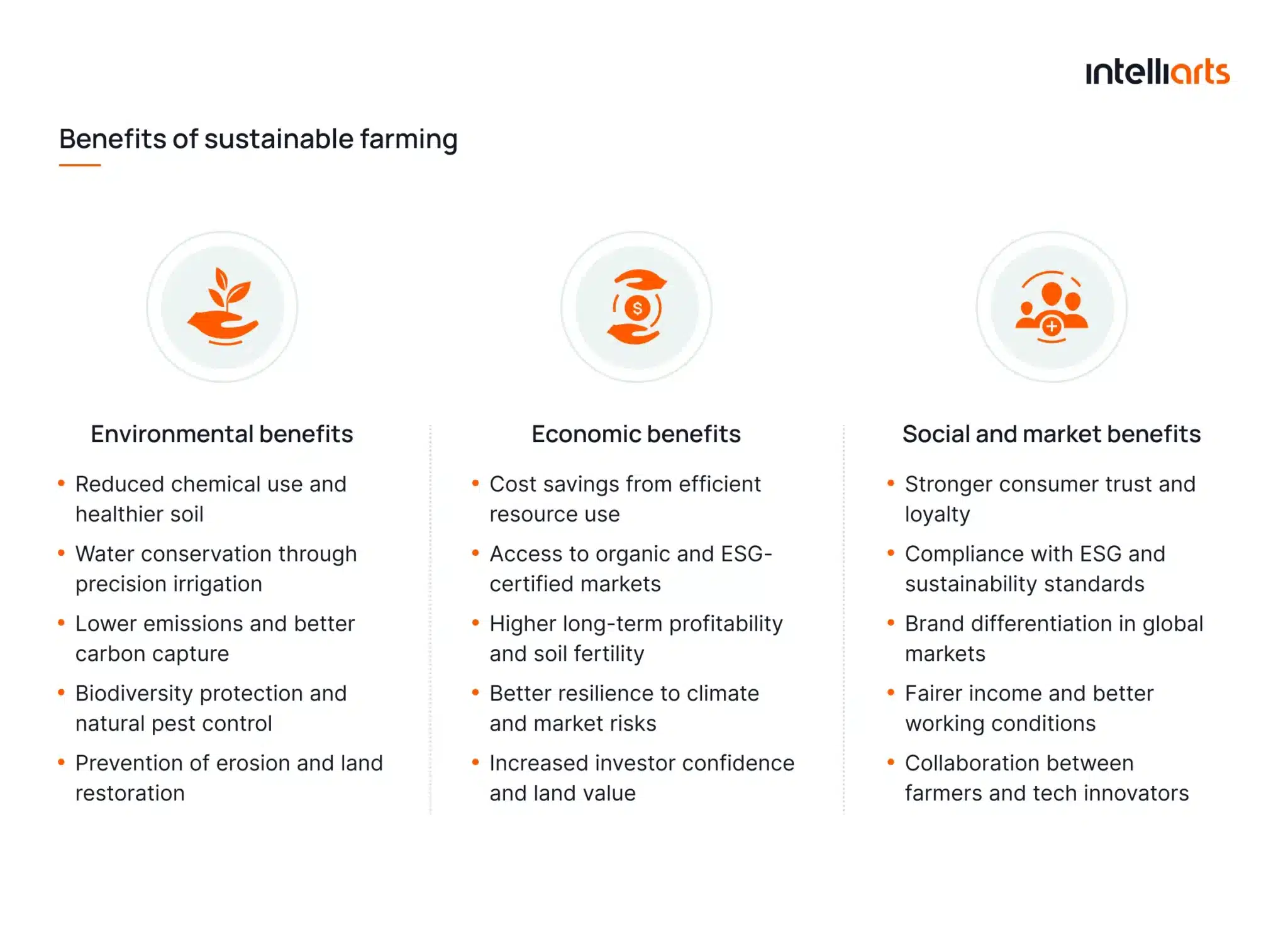
What are the benefits of sustainable farming?
Sustainable agriculture focuses on building a long-term balance between productivity, environmental care, and social responsibility. It ensures that farming remains viable for future generations while supporting the needs of today’s farmers and businesses. The benefits of sustainable farming can be seen across environmental, economic, and social dimensions.
Environmental benefits
Sustainable agriculture safeguards the planet’s natural systems and reduces the negative impact of farming on ecosystems. It emphasizes resource conservation, soil regeneration, and the responsible use of natural inputs.
Key environmental benefits of sustainable agriculture include:
- Reduced chemical use and healthier soil through crop rotation and composting.
- Water conservation with precision irrigation and moisture sensors.
- Lower emissions and improved carbon capture through regenerative practices.
- Biodiversity protection and natural pest control systems.
- Prevention of erosion and restoration of degraded land.
Sustainable agriculture focuses on ecosystem balance. At the same time, the balance benefits both productivity and the environment. Earthwatch Europe research indicated that sustainable farming positively impacts both the Earth and communities.
Economic benefits
From a financial perspective, sustainable agriculture offers opportunities for long-term stability and growth. A study on the costs and benefits of transition to sustainable agriculture shows positive transformations. As such, transitioning to sustainable agriculture requires upfront and ongoing costs, e.g, biodiversity features cost about $689/ha. Yet evidence shows lower fertiliser, pesticide, water, and fuel use, with stable or higher yields after 3–5 years and stronger long-term farm resilience.
Altogether, the major sustainable agriculture benefits include:
- Cost savings from reduced input use and efficient resource management.
- Access to new markets and certifications, such as organic and ESG-aligned supply chains.
- Long-term profitability through improved soil fertility and yield stability.
- Better resilience to climate risks and market fluctuations.
- Increased investor confidence and higher land value over time.
It’s worth noting that economic stability and environmental care are not separate goals, as they work together under the sustainable agriculture concept.
Social and market benefits
In a scientific review on the socio-economic performance of agroecology and farming, it’s shown that sustainability influences social and market dynamics. The impact focuses on strengthening relationships between producers and consumers and supporting community well-being.
Key advantages of sustainable agriculture include:
- Stronger consumer loyalty for eco-friendly, transparent production.
- Compliance with ESG reporting and sustainability policies.
- Brand differentiation for agribusinesses in competitive markets.
- Improved working conditions and fairer income distribution in rural areas.
- Enhanced collaboration between farmers, researchers, and tech innovators.
These outcomes explain why sustainable agriculture is so important. After all, it drives not just environmental recovery but also economic growth and social progress.
Don’t hesitate to additionally explore the benefits of precision farming.
Disadvantages of sustainable farming
While the benefits of sustainable agriculture are undeniable, the transition isn’t without its obstacles. Here are some limitations of sustainable farming, that every transitioning business should consider:
#1 Higher initial costs
Transitioning to sustainable agriculture often demands significant upfront investment. Farmers face expenses for:
- Modern equipment and precision tools
- Infrastructure upgrades (irrigation, storage, sensors)
- Certification and compliance processes
Without clear short-term ROI, many hesitate to adopt new systems despite long-term gains.
#2 Knowledge and skill gaps
Sustainable farming requires new competencies in data analysis, soil science, and eco-friendly techniques. Traditional farmers may struggle with:
- Data literacy for IoT or farm management software
- Understanding regenerative practices
- Access to proper training and expert support
These gaps can slow adoption and limit results.
#3 Lower short-term yields
During the early transition, yields may temporarily drop as soil ecosystems recover and new practices stabilize. This can create financial strain before benefits, like improved soil fertility and reduced input costs, become visible.
#4 Market and policy challenges
Sustainable products don’t always receive equal market access or policy backing. Many regions lack strong subsidies, consistent eco-labeling standards, or distribution networks for certified goods. This inconsistency complicates scaling sustainability efforts.
Data-driven decision making: Balancing the pros and cons of sustainable agriculture
Every innovation brings both opportunities and challenges. Sustainable agriculture is no exception. Farmers face high setup costs, complex data systems, and the need for specialized knowledge, yet the potential rewards include higher yields, lower waste, and long-term soil health.
Technology gives farmers data, but not direction. The real challenge is turning numbers into decisions that balance income, ecology, and time. — Yurii Bondarenko, Software Engineer at Intelliarts
Intelliarts bridges these challenges and opportunities through deep expertise in agricultural technology and data-driven transformation:
- Precision farming platforms & IoT integration: Intelliarts builds robust IoT-enabled systems that gather real-time field data from sensors, equipment and weather stations. This empowers your team to make informed decisions that reduce inputs and improve yields.
- AI & predictive analytics: Predictive analytics and other AI applications in agriculture forecast yields, predict pest outbreaks, and optimize resource inputs for maximum efficiency. With advanced machine-learning models, predictive analytics, and other AI applications in agriculture, Intelliarts helps forecast yields, anticipate pest or disease outbreaks and optimize resource usage for maximum efficiency.
- Farm management software: Intelliarts delivers custom farm management systems that integrate multiple data sources, streamline record-keeping, track costs and support sustainability compliance.
- Automation technologies: From equipment tracking solutions to land sampling automation, we help to implement automation and analytics related to labor-intensive tasks to scale your sustainable farming practices.
3x increase in final field acres and reduced data entry time from weeks to hours or even minutes are results you can expect, as an agriculture business, with Intelliarts.
Take a look at our grower data collection success story to explore another automation software example.
- Decision support systems (DSS): Intelliarts can develop custom scenario-modeling tools to guide planning and risk management. These systems help you respond proactively to changing field or market conditions.
The infographics below summarise this article’s insights on both physical and software technologies used in sustainable farming:
Here at Intelliarts, a trusted software development company, we have substantial expertise in addressing complex business challenges through technology. As provided above, we can help you make better use of physical devices for monitoring crops or soil, drones, green energy systems, and more. We do so by implementing decision-making, predictive analytics, automation, and other capabilities. We also have a strongly relevant domain expertise, acquired through working with companies like Indigo, an agritech innovator in the niche of farming and environmental sustainability.
Should you be interested in agriculture custom software development or technology consulting services, don’t hesitate to reach out.
Final take
Sustainable farming represents a strategic shift toward smarter, more resilient agriculture. It unites environmental care, economic stability, and social responsibility in one framework. With the right technology and expertise, the transition becomes both achievable and profitable.
With more than 24 years of experience delivering software solutions and a 90% customer return rate, Intelliarts can offer to transform a traditional farming business into a sustainable one. We can integrate advanced software, analytics, and automation tools that help agribusinesses make data-driven, sustainable decisions. We focus on long-term partnerships and are ready, willing, and able to contribute to your best project.
FAQ
Why is sustainable agriculture so important?
Sustainable agriculture is important because it ensures long-term food security, protects ecosystems, and supports rural economies. It uses resources efficiently, reduces soil degradation and emissions, and creates lasting positive impacts of agriculture on the environment while keeping farms productive for future generations.
What technologies are most useful for sustainable farming?
IoT sensors, AI analytics, and precision irrigation are the most effective tools for sustainable farming. They bring key benefits of sustainable agriculture by cutting waste, improving crop yields, and helping farmers protect soil health and biodiversity through smarter decisions.
What are the three main goals of sustainable agriculture?
The three main goals are environmental health, economic profitability, and social equity. Together, they reflect what is the main goal of sustainable agriculture, i.e., a balance between productivity, ecosystem protection, and community well-being.